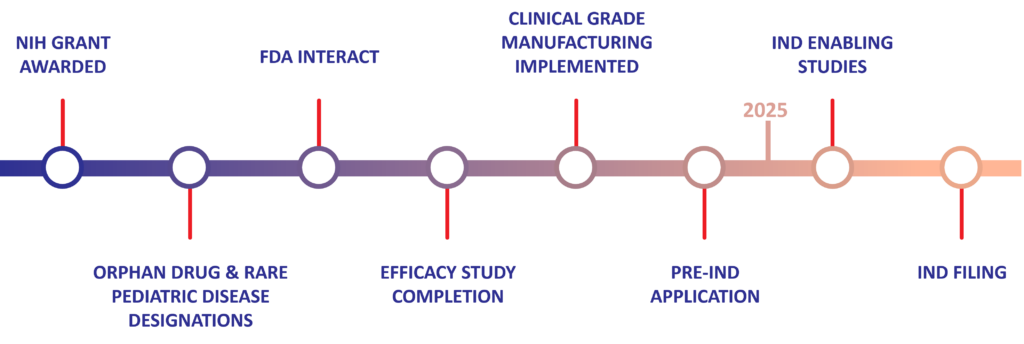
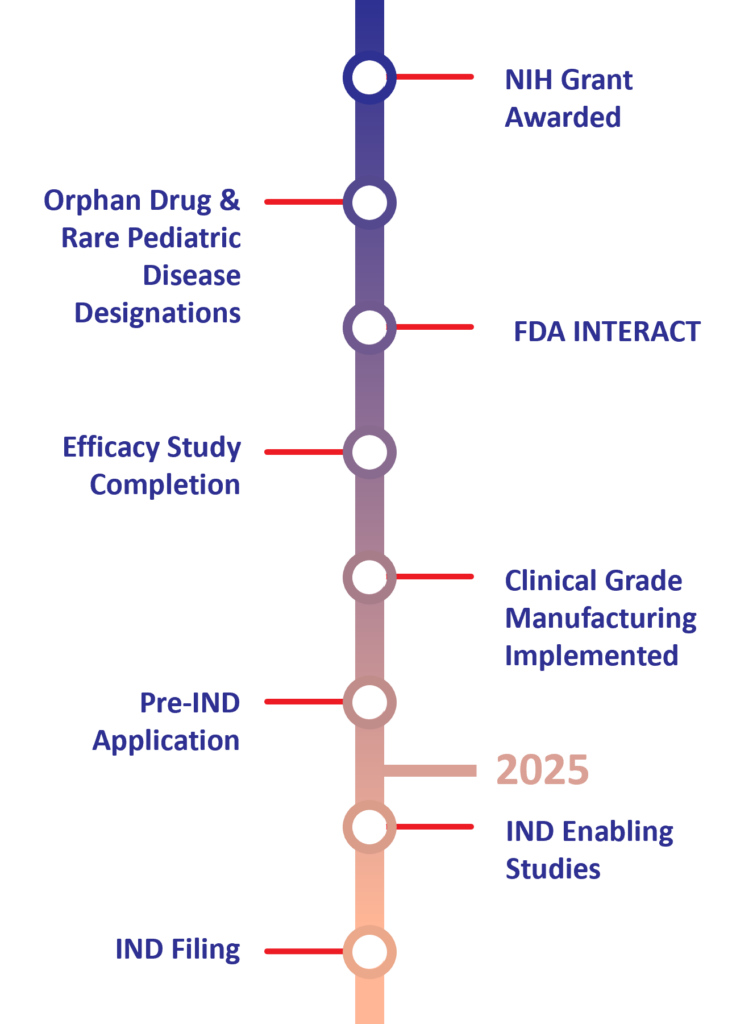
Human Placental Extract (HPE) Preclinical Milestones & Timeline

Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Pre-Clinical Efficacy
Reduction in NEC disease severity and number of affected regions in the gut with pre-treatment in a preclinical model of NEC.[1]
Mimicking Nature
High yield, consistent concentrations of proliferative, maturation, and immunomodulatory factors necessary to drive gut development.[1][3]
Safety
Compilation of naturally existing proteins needed during normal development in utero, and no safety or tolerability incidences during preclinical evaluation to preclude the use of HPE among babies at risk for NEC.
Lower Hospital Costs
Cost analysis of Neonatal ICU cost of care show reduced time in the NICU, fewer surgeries, and lower long-term comprehensive care for affected neonates.[2]
Osteoarthritis
Healthier Cartilage
Reduction in articulating cartilage damage following severe trauma in a preclinical model of ACL tear and meniscus damage. Increased proliferation of chondrocytes & cartilage explants in culture.[1]
Restorative
High yield, consistent concentrations of proliferative & immunomodulatory factors necessary to drive restore articulating cartilage.[1][4]
High Yield Consistency
Compilation of naturally-derived proteins prevents joint inflammation, unique to steroid, hyaluronic acid, platelet rich plasma and amniotic fluid.
Lower Hospital Costs
Improved outpatient treatment for joint injuries and prolonging time to joint replacement.[5]
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
References: (show)
- Data on file. Plakous Therapeutics.
- Mara KC, Clark RH, Carey WA. Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates: A Natural History Study. Am J Perinatol. 2022 Sep 16. doi: 10.1055/a-1851-1692. PMID: 35554890.
- Frost BL, Modi BP, Jaksic T, Caplan MS. New Medical and Surgical Insights Into Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Review. JAMA Pediatr. 2017 Jan 1;171(1):83-88. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.2708. PMID: 27893069.
- Vine JB, Apiliprantis AO, Gomoll AH, Farr J. Cryopreserved amniotic suspension for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. J Knee Surg. 2015;29(6):443-50.
- Carbone A, Rodeo S. Review of current understanding of post-traumatic osteoarthritis resulting from sports injuries. J Orthop Res. 2017 Mar;35(3):397-405. doi: 10.1002/jor.23341. Epub 2016 Jul 22. PMID: 27306867.
